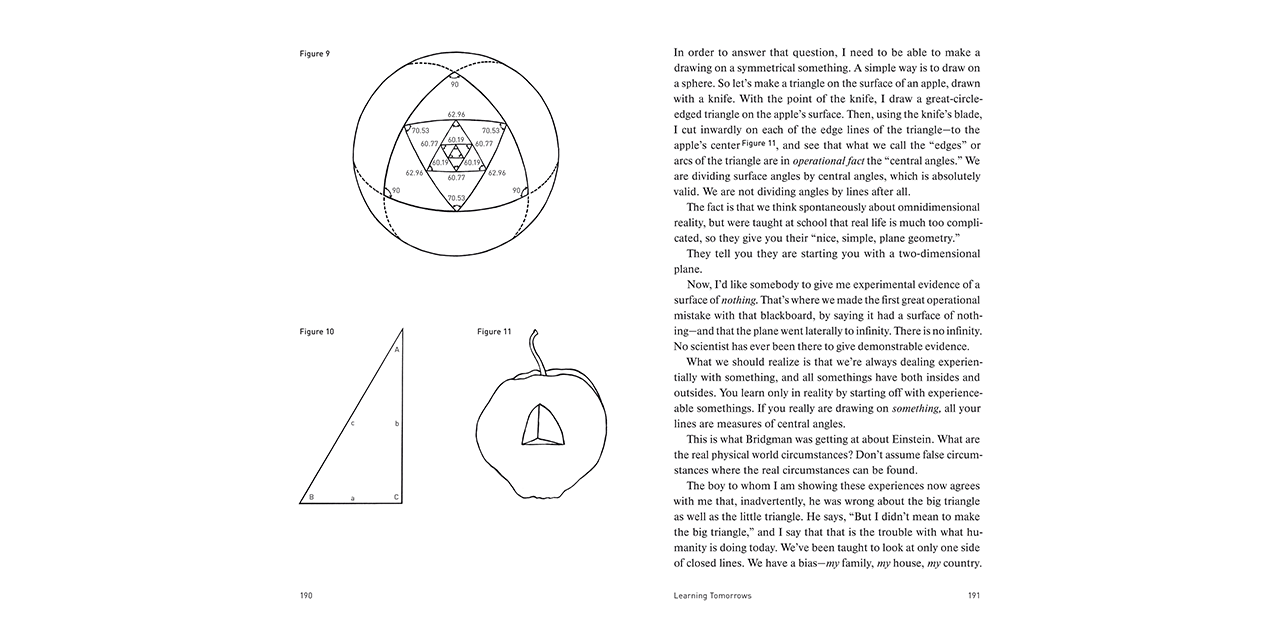
Education Automation
Buckminster Fuller’s prophetic 1962 book “Education Automation” brilliantly anticipated the need to rethink learning in light of a dawning revolution in informational technology – “upcoming major world industry.” Along with other essays on education, including “Breaking the Shell of Permitted Ignorance,” “Children: the True Scientists” and “Mistake Mystique” this volume presents a powerful approach for preparing ourselves to face epochal changes on spaceship earth: “whether we are going to make it or not... is really up to each one of us; it is not something we can delegate to the politicians – what kind of world are you really going to have?”
Richard Buckminster Fuller (1895–1983) was an architect and philosopher.
Buckminster Fuller’s prophetic 1962 book “Education Automation” brilliantly anticipated the need to rethink learning in light of a dawning revolution in informational technology – “upcoming major world industry.” Along with other essays on education, including “Breaking the Shell of Permitted Ignorance,” “Children: the True Scientists” and “Mistake Mystique” this volume presents a powerful approach for preparing ourselves to face epochal changes on spaceship earth: “whether we are going to make it or not... is really up to each one of us; it is not something we can delegate to the politicians – what kind of world are you really going to have?”
Richard Buckminster Fuller (1895–1983) was an architect and philosopher.